YEAR ফাংশন মাইক্রোসফট এক্সেলের একটি ডেট/টাইম ফাংশন যা একটি নির্দিষ্ট তারিখের বছর সংখ্যা রিটার্ন করে। এটি একটি তারিখের সিরিয়াল নম্বর গ্রহণ করে এবং 1900 থেকে 9999 এর মধ্যে একটি পূর্ণসংখ্যা রিটার্ন করে।

কেন ব্যবহার করা হয়?
YEAR ফাংশন বিভিন্ন ক্ষেত্রে ব্যবহার করা হয়, যেমন:
- ডেটা বিশ্লেষণ: YEAR ফাংশন ডেটা বিশ্লেষণের জন্য খুবই গুরুত্বপূর্ণ, বিশেষ করে যখন ডেটাতে তারিখ অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে। YEAR ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে, আপনি সহজেই ডেটা ট্রেন্ড, ঋতুগত পরিবর্তন, এবং অন্যান্য গুরুত্বপূর্ণ তথ্য সনাক্ত করতে পারেন।
- ডেটা ফিল্টারিং: YEAR ফাংশন ডেটা ফিল্টার করার জন্যও ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, আপনি YEAR ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে একটি নির্দিষ্ট বছরের মধ্যে সমস্ত ডেটা দেখাতে পারেন।
- ডেটা ম্যানিপুলেশন: YEAR ফাংশন ডেটা ম্যানিপুলেশনের জন্যও ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, আপনি YEAR ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে একটি তারিখের বছর পরিবর্তন করতে পারেন।
সুত্র/ফর্মুলা:
YEAR ফাংশনের সুত্র/ফর্মুলা হল:
YEAR(serial_number)
এখানে,
- serial_number: যে তারিখের বছর আপনি রিটার্ন করতে চান তার সিরিয়াল নম্বর।
উদাহরণ:
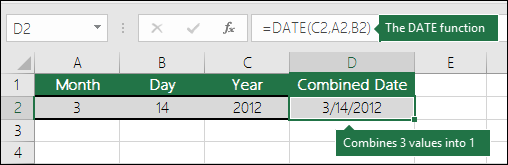
ধরুন, A1 সেলে “2024-03-31” তারিখটি রয়েছে। YEAR ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে, আপনি A1 সেলের বছর নিম্নলিখিত সূত্র ব্যবহার করে রিটার্ন করতে পারেন:
=YEAR(A1)এই সূত্রটি 2024 রিটার্ন করবে।
FAQ:
| প্রশ্ন | উত্তর |
|---|---|
| YEAR ফাংশন কিভাবে কাজ করে? | YEAR ফাংশন একটি নির্দিষ্ট তারিখের সিরিয়াল নম্বর গ্রহণ করে এবং 1900 থেকে 9999 এর মধ্যে একটি পূর্ণসংখ্যা রিটার্ন করে। |
| YEAR ফাংশনের সিনট্যাক্স কি? | YEAR ফাংশনের সিনট্যাক্স হল: YEAR(serial_number) |
| YEAR ফাংশনের কি কোনও বিকল্প আছে? | YEAR ফাংশনের কোনও বিকল্প নেই। |
| YEAR ফাংশন কোনও ত্রুটি রিটার্ন করে কি? | হ্যাঁ, YEAR ফাংশন নিম্নলিখিত ত্রুটিগুলি রিটার্ন করতে পারে: |
প্রশ্ন: YEAR ফাংশন কি 1900 সালের পূর্বের তারিখের জন্য কাজ করে?
উত্তর: না, YEAR ফাংশন 1900 সালের পূর্বের তারিখের জন্য কাজ করে না।
প্রশ্ন: YEAR ফাংশন কি টেক্সট তারিখের জন্য কাজ করে?
উত্তর: না, YEAR ফাংশন টেক্সট তারিখের জন্য কাজ করে না।
প্রশ্ন: YEAR ফাংশন কি তারিখের মাস বা দিনের মানকে প্রভাবিত করে?
উত্তর: না, YEAR ফাংশন শুধুমাত্র তারিখের বছরের মানকে প্রভাবিত করে।
প্রশ্ন: YEAR ফাংশনের বিকল্প কি?
উত্তর: YEAR ফাংশনের বিকল্প হল TEXT ফাংশন। TEXT ফাংশন “yyyy” ফর্ম্যাট ব্যবহার করে তারিখের বছর বের করতে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে।
- #VALUE!: যদি serial_number একটি বৈধ তারিখের সিরিয়াল নম্বর না হয়।
- #NUM!: যদি serial_number 1900 থেকে 9999 এর মধ্যে না থাকে।
উল্লেখ্য:
- YEAR ফাংশন শুধুমাত্র তারিখের বছর রিটার্ন করে।
- YEAR ফাংশন মাস, দিন, ঘন্টা, মিনিট, বা সেকেন্ড রিটার্ন করে না।
উল্লেখ্য:
- YEAR ফাংশন তারিখের সিরিয়াল নম্বর ব্যবহার করে কাজ করে।
- YEAR ফাংশনের ফলাফল একটি সংখ্যা।
- YEAR ফাংশন VBA-তেও ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে।
Description
Returns the year corresponding to a date. The year is returned as an integer in the range 1900-9999.
Syntax
YEAR(serial_number)
The YEAR function syntax has the following arguments:
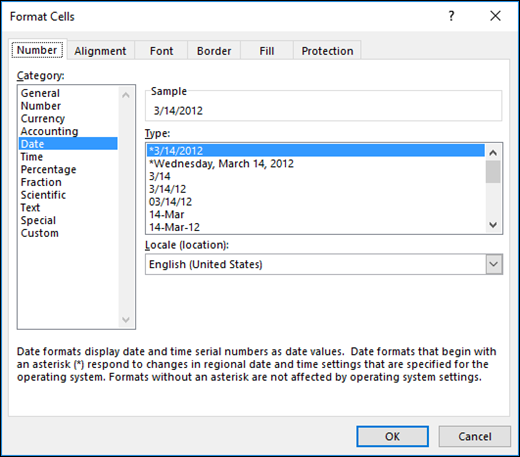
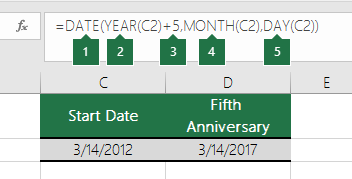
- Serial_number Required. The date of the year you want to find. Dates should be entered by using the DATE function, or as results of other formulas or functions. For example, use DATE(2008,5,23) for the 23rd day of May, 2008. Problems can occur if dates are entered as text.
Remarks
Microsoft Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers so they can be used in calculations. By default, January 1, 1900 is serial number 1, and January 1, 2008 is serial number 39448 because it is 39,448 days after January 1, 1900.
Values returned by the YEAR, MONTH and DAY functions will be Gregorian values regardless of the display format for the supplied date value. For example, if the display format of the supplied date is Hijri, the returned values for the YEAR, MONTH and DAY functions will be values associated with the equivalent Gregorian date.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
| Data | ||
| Date | ||
| 7/5/2008 | ||
| 7/5/2010 | ||
| Formula | Description (Result) | Result |
| =YEAR(A3) | Year of the date in cell A3 (2008) | 2008 |
| =YEAR(A4) | Year of the date in cell A4 (2010) | 2010 |