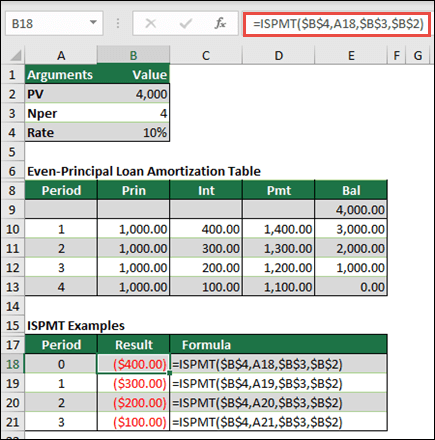
DOLLARDE ফাংশন হলো একটি Microsoft Excel ফাইন্যান্সিয়াল ফাংশন যা ডলার মূল্যকে ভগ্নাংশের সাথে দশমিক সংখ্যায় রূপান্তর করে। এটি প্রায়শই শেয়ারের মূল্যের মতো আর্থিক ডেটার সাথে কাজ করার সময় ব্যবহৃত হয়।
DOLLARDE ফাংশন কিভাবে কাজ করে?
DOLLARDE ফাংশন দুটি আর্গুমেন্ট গ্রহণ করে:
- Fractional_dollar: একটি ডলার মূল্য যা একটি পূর্ণসংখ্যা অংশ এবং একটি ভগ্নাংশ অংশ দ্বারা গঠিত।
- Fraction: ভগ্নাংশের হার।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি আপনি 1.02 কে 1/16 এর নির্ভুলতায় রূপান্তর করতে চান, তাহলে আপনি নিম্নলিখিত সূত্রটি ব্যবহার করবেন:
=DOLLARDE(1.02,16)
এই সূত্রটি 1.125 ফেরত দেবে। কারণ ভগ্নাংশের মান 16, তাই মূল্যটি 1/16 ডলারের নির্ভুলতায় রয়েছে।
DOLLARDE ফাংশন ব্যবহারের নিয়ম:
- DOLLARDE ফাংশন শুধুমাত্র Microsoft Excel 2007 বা তার পরবর্তী সংস্করণগুলিতে উপলব্ধ।
- Fractional_dollar আর্গুমেন্ট একটি সংখ্যা হতে হবে যা একটি পূর্ণসংখ্যা অংশ এবং একটি ভগ্নাংশ অংশ দ্বারা গঠিত।
- Fraction আর্গুমেন্ট একটি ধনাত্মক পূর্ণসংখ্যা হতে হবে।
- যদি Fractional_dollar আর্গুমেন্ট একটি নেতিবাচক সংখ্যা হয়, তাহলে DOLLARDE #NUM! এরর ফেরত দেবে।
- যদি Fraction আর্গুমেন্ট 0 হয়, তাহলে DOLLARDE #DIV/0! এরর ফেরত দেবে।
- যদি Fractional_dollar আর্গুমেন্ট একটি ভগ্নাংশ না হয়, তাহলে DOLLARDE #VALUE! এরর ফেরত দেবে।
DOLLARDE ফাংশন ব্যবহারের উদাহরণ:
গল্প:
শুভ্র একটি শেয়ারবাজার ব্রোকার। সে একজন গ্রাহকের জন্য 100 টি শেয়ার কিনতে চায় যার প্রতিটি শেয়ারের মূল্য 16 5/16 ডলার। শুভ্রকে মোট কত টাকা খরচ করতে হবে তা নির্ণয় করতে হবে।
সমাধান:
শুভ্র DOLLARDE ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে মোট মূল্য গণনা করতে পারে।
=100 * DOLLARDE(16.3125,16)
এই সূত্রটি 1631.25 ফেরত দেবে। অর্থাৎ, শুভ্রকে মোট 1631.25 ডলার খরচ করতে হবে।
উপসংহার:
DOLLARDE ফাংশন হলো একটি সহজ এবং কার্যকর ফাংশন যা ডলার মূল্যকে ভগ্নাংশের সাথে দশমিক সংখ্যায় রূপান্তর করতে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে। এটি শেয়ারবাজার, বন্ড এবং অন্যান্য আর্থিক ডেটার সাথে কাজ করার সময় বিশেষভাবে সহায়ক।
Description
Converts a dollar price expressed as an integer part and a fraction part, such as 1.02, into a dollar price expressed as a decimal number. Fractional dollar numbers are sometimes used for security prices.
The fraction part of the value is divided by an integer that you specify. For example, if you want your price to be expressed to a precision of 1/16 of a dollar, you divide the fraction part by 16. In this case, 1.02 represents $1.125 ($1 + 2/16 = $1.125).
Syntax
DOLLARDE(fractional_dollar, fraction)
The DOLLARDE function syntax has the following arguments:
- Fractional_dollar Required. A number expressed as an integer part and a fraction part, separated by a decimal symbol.
- Fraction Required. The integer to use in the denominator of the fraction.
Remarks
- If fraction is not an integer, it is truncated.
- If fraction is less than 0, DOLLARDE returns the #NUM! error value.
- If fraction is greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1, DOLLARDE returns the #DIV/0! error value.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =DOLLARDE(1.02,16) | Converts 1.02, read as 1 and 2/16, to a decimal number (1.125). Because the fraction value is 16, the price has a precision of 1/16 of a dollar. | 1.125 |
| =DOLLARDE(1.1,32) | Converts 1.1, read as 1 and 10/32, to a decimal number (1.3125). Because the fraction value is 32, the price has a precision of 1/32 of a dollar. | 1.3125 |
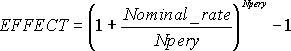
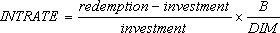 where:
where: