The Simple Past Tense, also referred to as the Past Simple Tense, is a grammatical structure used to express actions or events that occurred and were completed in the past. It is a fundamental tense in English grammar that allows us to recount past experiences, narrate stories, and discuss historical events. By understanding and utilizing the Simple Past Tense correctly, we can effectively communicate about past actions and their timing. In this article, we will explore the definition, usage, and examples of the Simple Past Tense, providing you with a solid foundation to master this essential aspect of the English language.
What is Simple Past Tense:
The Past Simple Tense is a verb tense that signifies actions or events that took place at a specific time in the past. It emphasizes that the action is no longer ongoing and has been completed. This tense allows us to communicate about past situations, experiences, or states of being.
Structure of Simple Past Tense:
To construct the Past Simple Tense, regular verbs require the addition of “-ed” to the base form of the verb. However, irregular verbs have unique past tense forms that must be memorized. The structure of the Past Simple Tense is as follows:
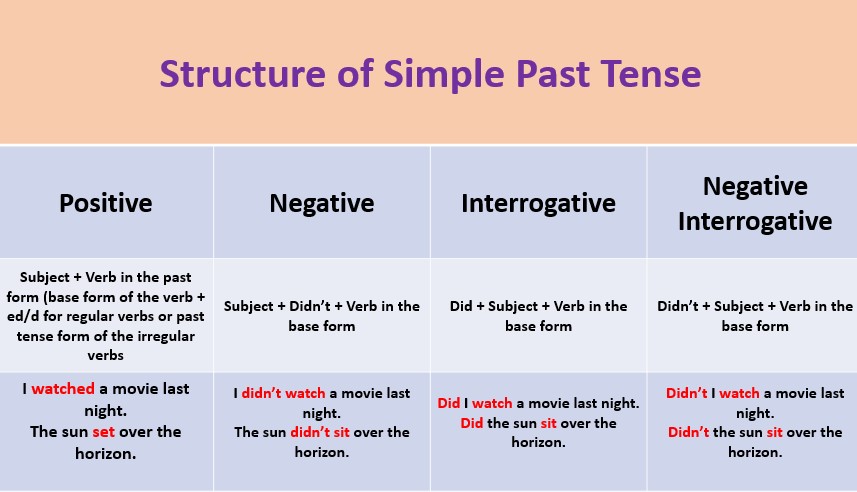
1. Positive Sentence:
Subject + Verb in the past form (base form of the verb + ed/d for regular verbs or past tense form of the irregular verbs
Example:
- I visited my grandparents last weekend.
- They bought a new car yesterday.
- She graduated with honors from the university.
- He received a promotion at work.
- We celebrated our anniversary at a fancy restaurant.
- The concert was amazing. They played all my favorite songs.
- I finished reading an interesting book last night.
- They completed the project ahead of schedule.
- She won the first prize in the art competition.
- We hiked to the top of the mountain and enjoyed the breathtaking view.
In each of these sentences, the verbs are in the past tense form, indicating completed actions or events that occurred in the past.
2. Negative Sentence:
Subject + Didn’t + Verb in the base form
Example:
- I didn’t see him at the party last night.
- They didn’t finish their homework on time.
- She didn’t pass the exam despite studying hard.
- He didn’t enjoy the movie; it was too long and boring.
- We didn’t go on a vacation this summer.
- The restaurant didn’t have vegetarian options on the menu.
- I didn’t receive a reply to my email.
- They didn’t win the game; the opposing team scored more goals.
- She didn’t attend the meeting due to a scheduling conflict.
- We didn’t have any luck finding parking near the event venue.
In each of these sentences, the word “didn’t” is used to indicate the negation or absence of the action or event in the past.
3. Interrogative Structure:
Did + Subject + Verb in the base form
Example:
- Did you finish your homework yesterday?
- Did they visit Paris during their summer vacation?
- Did she complete the project on time?
- Did he watch the movie last night?
- Did we go to the beach last weekend?
- Did the team win the championship last year?
- Did you have a good time at the party?
- Did they find what they were looking for?
- Did she attend the conference last week?
- Did we meet each other before?
In each of these sentences, the word “did” is used to form the interrogative structure in the past tense, indicating that the action or event is being questioned.
4. Negative Interrogative Structure:
Didn’t + Subject + Verb in the base form
Example:
- Didn’t you finish your homework yesterday?
- Didn’t they visit Paris during their summer vacation?
- Didn’t she complete the project on time?
- Didn’t he watch the movie last night?
- Didn’t we go to the beach last weekend?
- Didn’t the team win the championship last year?
- Didn’t you have a good time at the party?
- Didn’t they find what they were looking for?
- Didn’t she attend the conference last week?
- Didn’t we meet each other before?
In each of these sentences, the word “didn’t” is used to form the negative interrogative structure in the past tense, indicating that the action or event is being questioned in the negative form.
Rules of Simple Past Tense:
- Regular Verbs: For regular verbs, the simple past tense is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- Base form: talk / Simple past: talked
- Base form: walk / Simple past: walked
- Irregular Verbs: Irregular verbs have unique forms in the simple past tense, which do not follow the regular “-ed” pattern. These forms must be memorized. For example:
- Base form: go / Simple past: went
- Base form: see / Simple past: saw
- Negative Sentences: To form a negative sentence in the simple past tense, use the auxiliary verb “did” in its past tense form, followed by “not” (didn’t), and the base form of the main verb. For example:
- I didn’t go to the party.
- Questions: To form a question in the simple past tense, invert the subject and the auxiliary verb “did” in its past tense form, and use the base form of the main verb. For example:
- Did you watch the movie?
- Time Expressions: The simple past tense is commonly used with time expressions that indicate a specific point in the past, such as yesterday, last week, or 1990. For example:
- She finished her work yesterday.
- They traveled to Europe last summer.
- Past Habitual Actions: The simple past tense can also be used to talk about habitual actions or repeated events in the past. For example:
- We often played soccer together.
Remember that there are additional rules and exceptions to consider when using the simple past tense, such as spelling changes for certain verbs or irregularities in pronunciation. It’s always helpful to consult a reliable grammar resource for a more comprehensive understanding.
Use of Simple past Tense:
The simple past tense is used to talk about completed actions or events that occurred at a specific time in the past. Here are some common uses of the simple past tense:
- Narrating Past Events: The simple past tense is frequently used in storytelling or when recounting events that took place in the past. For example:
- She walked to the store and bought some groceries.
- They visited their grandparents over the weekend.
- Describing Past Experiences: When discussing personal experiences or actions that happened in the past, the simple past tense is employed. For instance:
- I traveled to Japan last year.
- He studied French in college.
- Stating Past Facts or Generalizations: The simple past tense can be used to state facts or make generalizations about the past. For example:
- Thomas Edison invented the light bulb.
- Dogs were domesticated thousands of years ago.
- Expressing Past Habits or Routines: When discussing habitual or regular actions in the past, the simple past tense is employed. For example:
- She always drank a cup of tea in the morning.
- We went for a walk every evening.
- Reporting Direct Speech: The simple past tense is used to report or convey statements or actions directly spoken in the past. For example:
- She said, “I finished my work.”
- He asked, “Did you see the movie?”
- Referring to Specific Time in the Past: The simple past tense is used when referring to a specific time or duration in the past. For example:
- We went to the beach last summer.
- The concert started at 8 p.m.
Remember to use the simple past tense when the action or event occurred and was completed in the past, and pay attention to the context and time frame of the sentence.
She _______________ her favorite book last night. (read)
Answer: She read her favorite book last night.
We _______________ a delicious dinner at the new restaurant. (have)
Answer: We had a delicious dinner at the new restaurant.
3. He _______________ his bike to school yesterday. (ride)
Answer: He rode his bike to school yesterday.
They _______________ a great time at the party. (have)
Answer: They had a great time at the party.
I _______________ my keys on the kitchen counter. (leave)
Answer: I left my keys on the kitchen counter.
The cat _______________ up a tree and couldn’t get down. (climb)
Answer: The cat climbed up a tree and couldn’t get down.
She _______________ a beautiful song at the concert. (sing)
Answer: She sang a beautiful song at the concert.
They _______________ their old house and moved to a new city. (sell)
Answer: They sold their old house and moved to a new city.
We _______________ a long walk on the beach yesterday. (take)
Answer: We took a long walk on the beach yesterday.
He _______________ a picture of the sunset. (take)
Answer: He took a picture of the sunset.
The students _______________ hard for the exam. (study)
Answer: The students studied hard for the exam.
She _______________ the answer to the question. (know)
Answer: She knew the answer to the question.
They _______________ a fantastic vacation in Hawaii. (have)
Answer: They had a fantastic vacation in Hawaii.
I _______________ a new bicycle for my birthday. (get)
Answer: I got a new bicycle for my birthday.
We _______________ to the park and played frisbee. (go)
Answer: We went to the park and played frisbee.
He _______________ his favorite team win the championship. (watch)
Answer: He watched his favorite team win the championship.
They _______________ their parents to visit them last summer. (invite)
Answer: They invited their parents to visit them last summer.
She _______________ a delicious cake for the party. (bake)
Answer: She baked a delicious cake for the party.
We _______________ an interesting documentary on TV. (watch)
Answer: We watched an interesting documentary on TV.
He _______________ a new job last month. (start)
Answer: He started a new job last month.
Here are some fill-in-the-blank sentences for you to test your understanding of the simple past tense. The answers are provided below each sentence:
Leave a Reply