The Simple Present Tense, also known as the Present Indefinite Tense, is used to describe actions or events that occur in the present or actions that are true in general. It is commonly used to express routines, habits, general facts, and permanent situations. The verb in this tense takes the base form or the ‘s’ form for third-person singular subjects.
What is Simple Present Tense?
The Simple Present Tense refers to the tense used to describe events, actions, and conditions that are happening all the time or exist in the present. It is used to talk about things that happen regularly or situations that exist at this time.
The simple present tense is formed by using the base form of the verb (also known as the infinitive) without any endings or auxiliary verbs, except for the third person singular where an ‘s’ or ‘es’ is added to the verb.
Structure of the Simple Present Tense:
The structure of the Simple Present Tense can be understood by analyzing the positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative forms of the tense. Here is the structure chart:
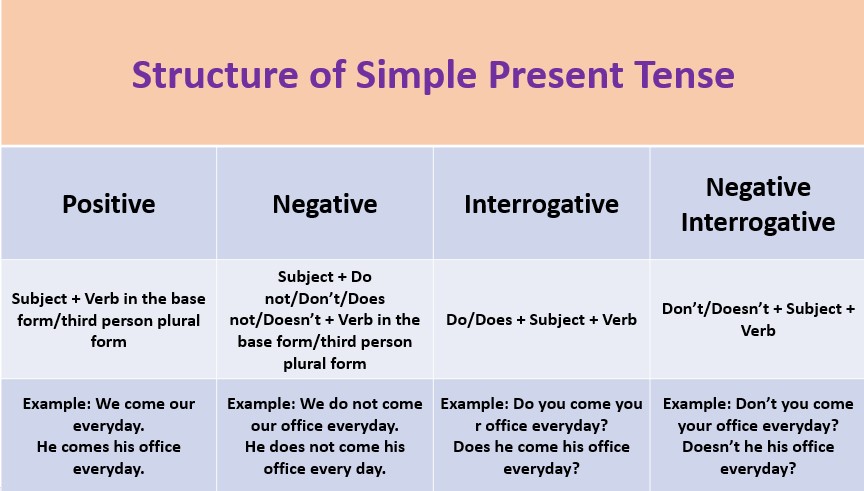
1. Positive Structure
Subject + Verb (base form/third person plural form) + Rest of the sentence
Examples:
- I like to read books.
- She plays the piano beautifully.
- They live in a big house.
- We enjoy going to the beach.
- The sun rises in the east.
- He teaches English at the university.
- Cats love to chase mice.
- We visit our grandparents every weekend.
- Dogs bark when they see strangers.
- The train arrives at 7 PM.
2. Negative Structure:
Subject + Do not/Don’t/Does not/Doesn’t + Verb (base form/third person plural form) + Rest of the sentence
Examples:
- I do not like spicy food.
- She doesn’t watch TV in the morning.
- They don’t eat meat.
- We do not play football on Sundays.
- He doesn’t speak Spanish fluently.
- Cats do not like water.
- They don’t believe in ghosts.
- I do not drink coffee.
- She doesn’t enjoy going to crowded places.
- We don’t need any help.
3. Interrogative Structure:
Do/Does + Subject + Verb (base form/third person plural form) + Rest of the sentence
Examples:
- Do you like ice cream?
- Does she speak French fluently?
- Do they study together?
- Does he play the guitar?
- Do you enjoy watching movies?
- Does it rain a lot in your city?
- Do they have a pet dog?
- Does she know how to swim?
- Do you prefer tea or coffee?
- Does he go to the gym regularly?
4. Negative Interrogative Structure:
Don’t/Doesn’t + Subject + Verb (base form/third person plural form) + Rest of the sentence
Examples:
- Don’t you like pizza?
- Doesn’t she understand the instructions?
- Don’t they enjoy going to parties?
- Doesn’t he know the answer?
- Don’t you play any musical instruments?
- Doesn’t it get cold in the winter?
- Don’t they live in that neighborhood anymore?
- Doesn’t she speak English fluently?
- Don’t you want to join us for dinner?
- Doesn’t he like spicy food?
By understanding the structure of the Simple Present Tense in its various forms, you can effectively construct sentences and communicate your thoughts and ideas in English. Practice using these structures with different verbs and subjects to improve your proficiency in the language.
Rules of Simple Present Tense:
- For the third person singular, add an ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the base form of the verb. Exceptions to this rule include verbs ending in ‘-s’, ‘-x’, ‘-z’, ‘-ch’, or ‘-sh’ where an ‘es’ is added to the verb instead of ‘s’.
Example: She studies hard for her exams. (add ‘es’ to ‘study’)
- In negative and question sentences, the auxiliary verb ‘do/does’ is added before the base form of the verb to indicate the present tense.
Example: They do not watch TV in the morning.
- For verbs ending in ‘-y’ preceded by a consonant, change the ‘y’ to ‘i’ and add ‘es’ in the third person singular.
Example: He studies hard for his exams. (change ‘y’ to ‘i’ and add ‘es’ to ‘study’)
Uses of Simple Present Tense:
- To state general truths and scientific facts:
- The Earth revolves around the sun.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- To denote habitual or repeated actions:
- I go to the gym every morning.
- They often visit their grandparents on weekends.
- To indicate unchanging events or permanent situations:
- She works as a nurse.
- The restaurant opens at 7 AM.
- To give directions or instructions:
- Take the second left and then turn right at the traffic light.
- Close the door before leaving the room.
- To express future events in a scheduled or fixed timetable:
- The train departs at 9 PM tomorrow.
- Our flight arrives on Friday morning.
Here are some fill-in-the-blank sentences to test your understanding of the Simple Present Tense:
- My parents _______ (live) in a small town.
- We _______ (study) English every day.
- Sarah _______ (play) the guitar beautifully.
- They _______ (go) to the gym regularly.
- The sun _______ (rise) in the east.
- I _______ (enjoy) watching movies on weekends.
- Tom and Emily _______ (work) in the same office.
- She _______ (speak) three languages fluently.
- We _______ (have) dinner at 7 PM every evening.
- The cat _______ (sleep) on the sofa.
Answers:
- My parents live in a small town.
- We study English every day.
- Sarah plays the guitar beautifully.
- They go to the gym regularly.
- The sun rises in the east.
- I enjoy watching movies on weekends.
- Tom and Emily work in the same office.
- She speaks three languages fluently.
- We have dinner at 7 PM every evening.
- The cat sleeps on the sofa.
In summary, the simple present tense is used to describe actions, situations, or habits that are happening now, regularly, or as a general truth. It’s a simple and versatile tense that is widely used in everyday conversation and writing.
Leave a Reply